Prerequisites
Before you add a Snowflake connection, ensure the default role of the account being used has been granted usage on the database and the schema, and select on the tables that will be added to the connection.
Example:
- Grant usage on database
<databasename>to role<rolename> - Grant usage on schema
<databasename>.<schemaname>to role<rolename> - Grant select on all tables in schema
<databasename>.<schemaname>to role<rolename>
Connecting to Snowflake
To connect to Snowflake:
-
Click Data in the top navigation bar.
-
Click the Connections tab at the top of the page, and click + Add connection at the upper-right-hand side of the page.
-
Create a name for your connection, a description (optional), then select the Snowflake connection type, and click Continue.
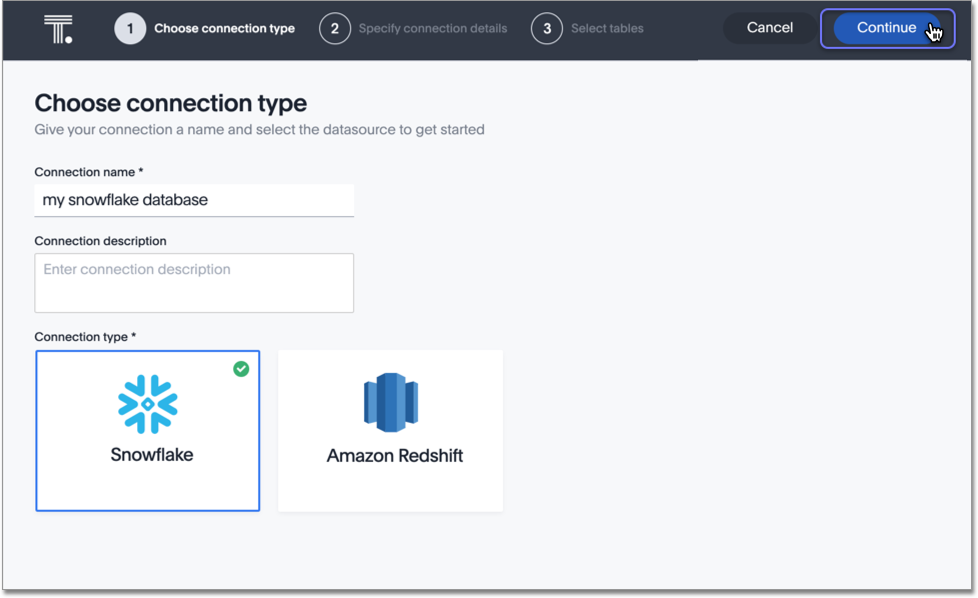
-
Enter the connection details for your Snowflake data source using either OAuth, Microsoft Azure AD OAuth, or Service Account authentication:
The Use OAuth option uses Snowflake OAuth authentication.
Before selecting Use OAuth authentication, you must configure OAuth in Snowflake. For details, see Configure OAuth for a Snowflake connection.
Before selecting Microsoft Azure AD OAuth authentication, you must configure Azure AD external OAuth. For details, see Configure Azure AD external OAuth for a Snowflake connection.
For OAuth authentication, do the following:
- Select Use OAuth.
- Enter Account name or your Snowflake URL, OAuth Client ID, OAuth Client Secret, and (optional) Database.
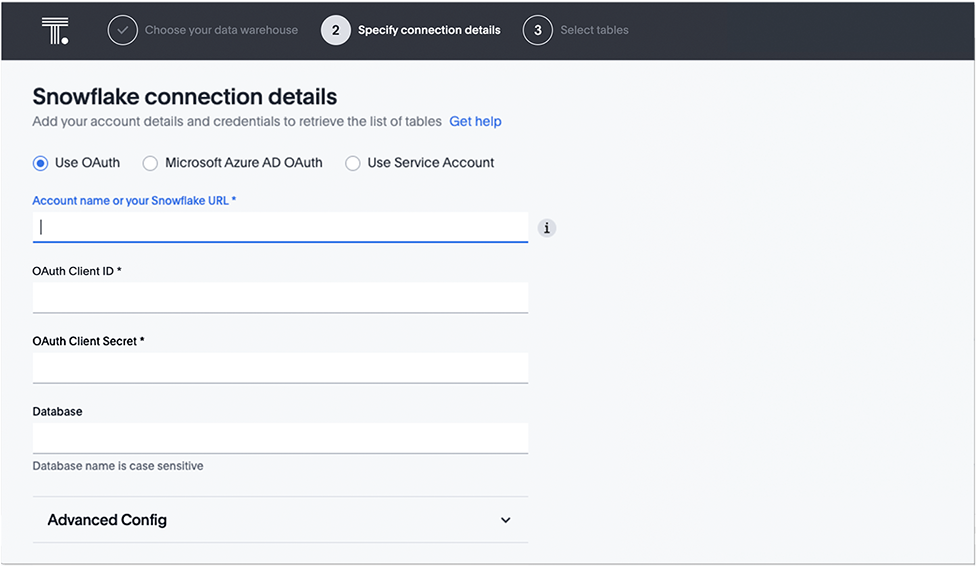
- If you wish to provide the optional additional key-value pairs for your Snowflake connection, complete the procedure in step 5, and then click Continue. If not, click Continue.
- When the Snowflake login screen appears, enter your Snowflake User Name and Password and click Log In, or use the Single-Sign-On option.
-
In the next Snowflake screen, allow ThoughtSpot to access your Snowflake account by clicking Allow, and then go to step 7 to select tables for your connection.
Using security passthrough may have implications for your Row Level Security. See About row level security (RLS) for more information.
For Microsoft Azure AD OAuth authentication, do the following:
- Select Microsoft Azure AD OAuth.
- Enter Account name or Snowflake URL, OAuth Client ID, OAuth Client Secret, Scope, Auth URL, Access token URL, and (optional) Database.
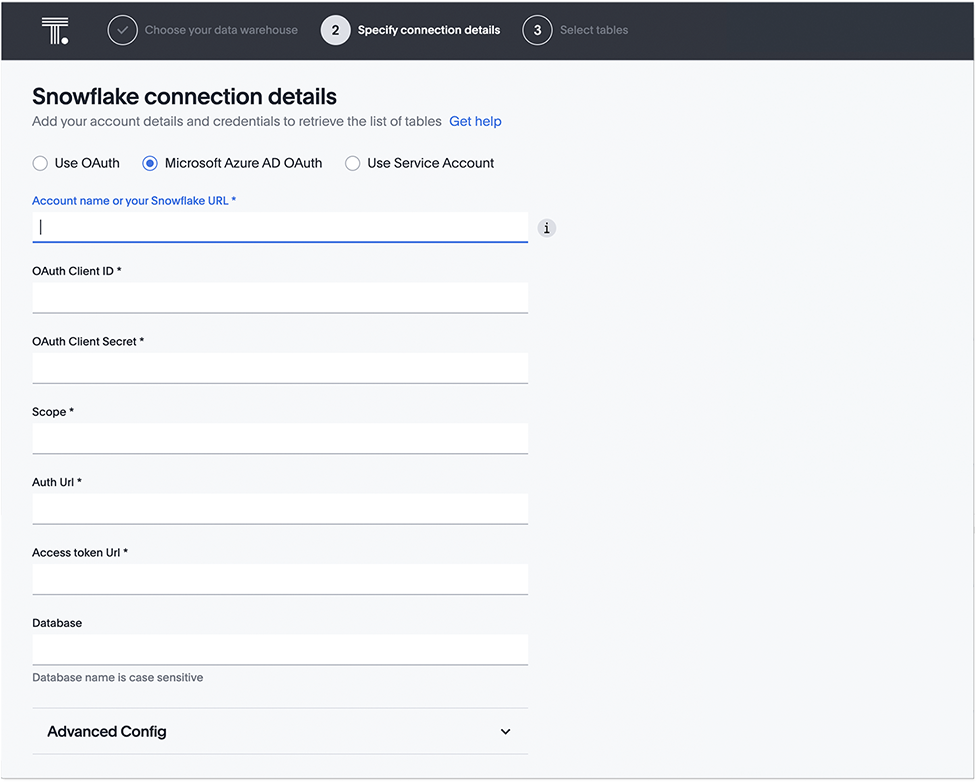
- If you wish to provide the optional additional key-value pairs for your Snowflake connection, complete the procedure in step 5, and then click Continue. If not, click Continue.
- When the Microsoft sign-in screen appears, sign in to your account using the email and password of your Microsoft account associated with Azure.
- On the Stay-signed-in screen, click Yes.
For Use Service Account authentication, do the following:
- Select Use Service Account.
- Enter Account name, User, Password, Role, Warehouse, and (optional) Database.
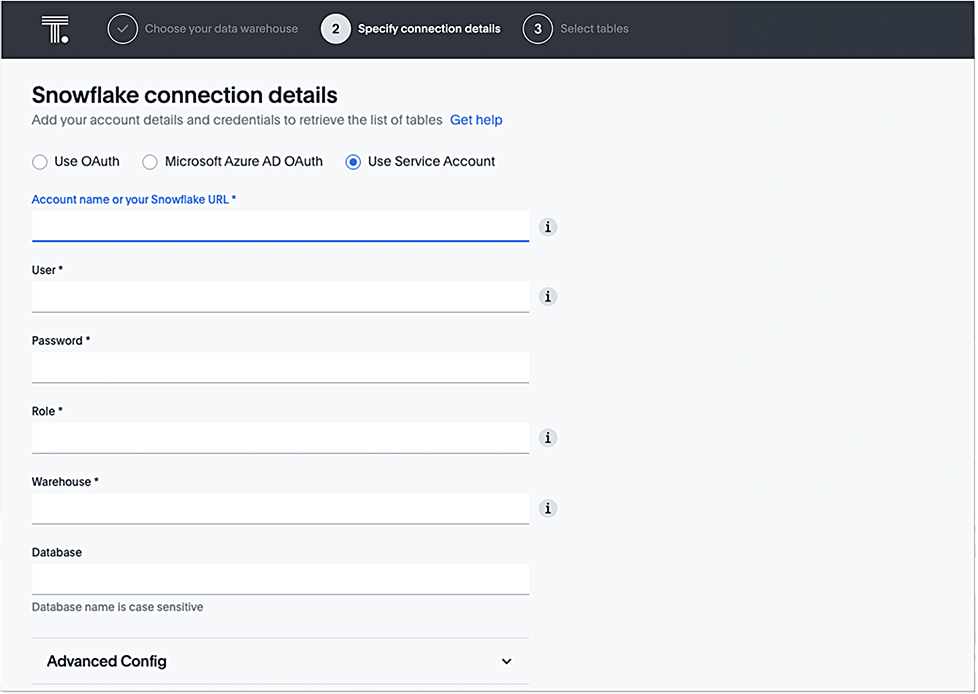
Refer to the Snowflake connection reference for more information on each of the specific attributes you must enter for your connection.
-
(Optional) Provide additional key-value pairs that are required to set up your connection to Snowflake, by doing the following:
- Click the Advanced Config menu to reveal the Key and Value fields.
- Enter your key and value information.
- To add more keys and values, click the plus sign (+), and enter them.
Note: Any key-value pairs that you enter must be defined in your Snowflake data source. Key-value pairs are case-sensitive. -
Click Continue.
-
Select tables (on the left) and the columns from each table (on the right), and then click Create connection.
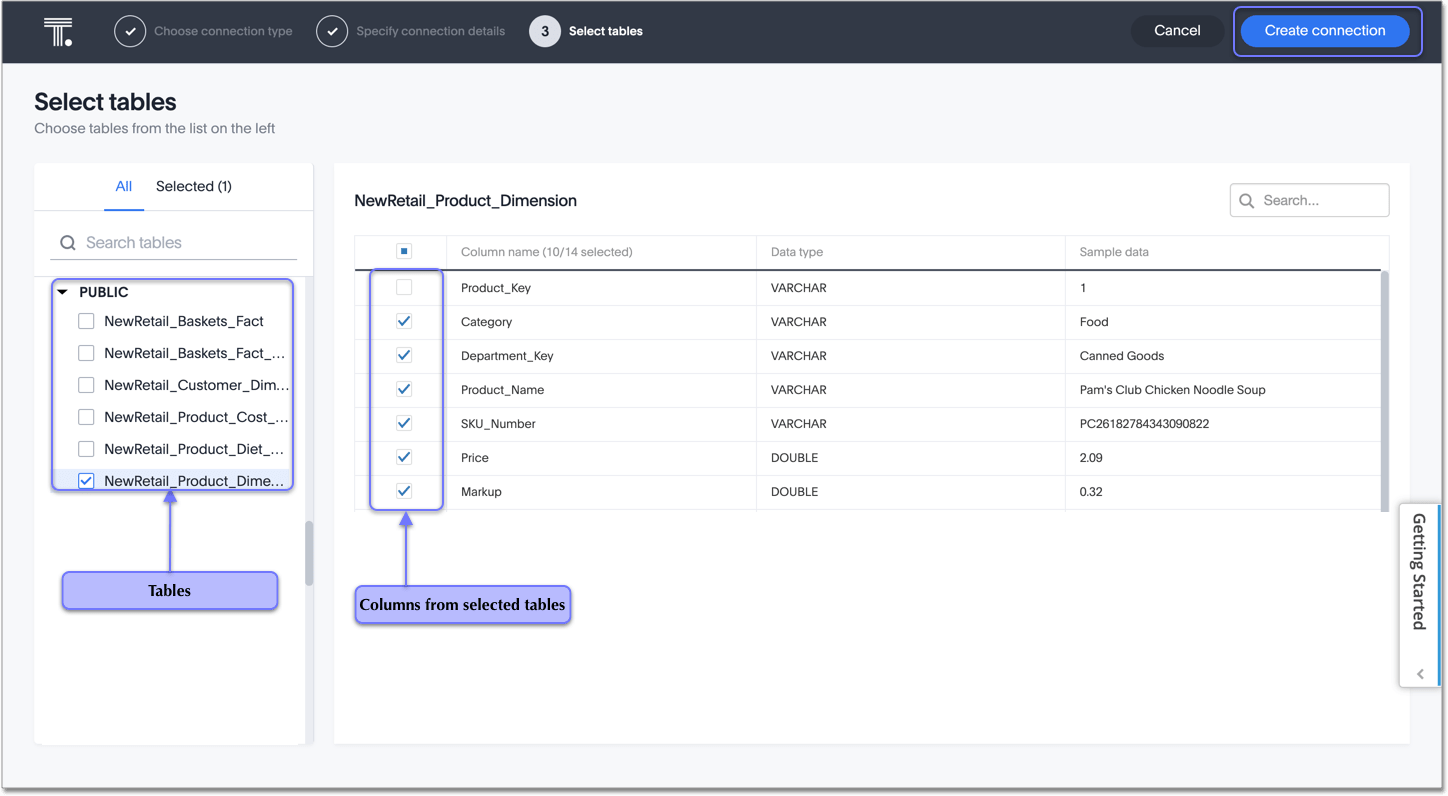
The Create connection message appears, telling you the number of tables and columns that will be added to your connection.
-
Click Create.
After you add the connection, you can search your Snowflake database using the Search field.
Your new connection appears on the Data > Connections page. You can click the name of your connection to view the tables and columns in your connection.
The connection you just created is a link to the external data source. If there are any joins in the selected tables of the external data source, those are imported into ThoughtSpot.
You can now perform a live query on the selected tables and columns of your connection. Because the selected tables and columns in your connection are linked, it may take a while to initially render the search results. This is because ThoughtSpot does not cache linked data. With linked data, ThoughtSpot queries the external database directly, which is slower than querying data that is stored in ThoughtSpot’s database.
You can modify a Snowflake connection in the following ways:
- Edit a Snowflake connection
- Remap a Snowflake connection
- Delete a table from a Snowflake connection
- Delete a table with dependent objects
You can also Delete a Snowflake connection.
See the Connection reference for details of connection parameters.
We also recommend that you review Best Practices for Snowflake connections